🧠 TABLE OF CONTENT
The Dangers of Brain Aneurysm
Types of Brain Aneurysms
Symptoms of Brain Aneurysms
When to Seek Medical Attention
FAQs
Key Takeaway:
- Understanding Aneurysms: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
- A brain aneurysm is a weak area in the wall of a blood vessel that can bulge or balloon out and has the potential to rupture, causing a potentially life-threatening condition.
- Brain aneurysms can form due to various factors, including genetic predisposition, high blood pressure, smoking, and certain medical conditions. Understanding the risk factors can help identify individuals at higher risk and preventative measures.
- If a brain aneurysm ruptures, it can lead to serious complications, such as subarachnoid hemorrhage, which requires immediate medical attention. Recognizing the symptoms of a ruptured aneurysm is crucial for prompt treatment.
- Screening for brain aneurysms is important, especially for individuals with a family history or specific risk factors. Early detection can allow for preventive measures or timely treatment.
- There are different types of brain aneurysms, including saccular aneurysms (berry aneurysms), fusiform aneurysms, and mycotic aneurysms. Understanding the types can help in diagnosis and treatment planning.
- The symptoms of brain aneurysms can vary depending on whether the aneurysm is unruptured, ruptured, or leaking. Recognizing these symptoms can aid in seeking medical attention in a timely manner.
- When experiencing symptoms of a ruptured aneurysm, it is essential to seek immediate medical attention. Time is crucial for the best chance of successful treatment and recovery.
- Treatment options for brain aneurysms may include observation, medication, endovascular procedures, or surgical intervention, depending on the size, location, and overall health of the patient.
The Dangers of Brain Aneurysm
When it comes to the dangers of brain aneurysms, there is much to explore. A brain aneurysm is a serious condition that can have devastating consequences if left untreated. Understanding what a brain aneurysm is and how it forms is crucial in recognizing the potential risk.
The question arises: what happens when a brain aneurysm ruptures? The consequences can be life-threatening and immediate medical attention is essential.
Lastly, the importance of screening for brain aneurysms cannot be overstated. Detecting and treating an aneurysm before it ruptures can significantly improve outcomes.
So, let's dive into this topic to gain a deeper understanding and shed light on these vital aspects.
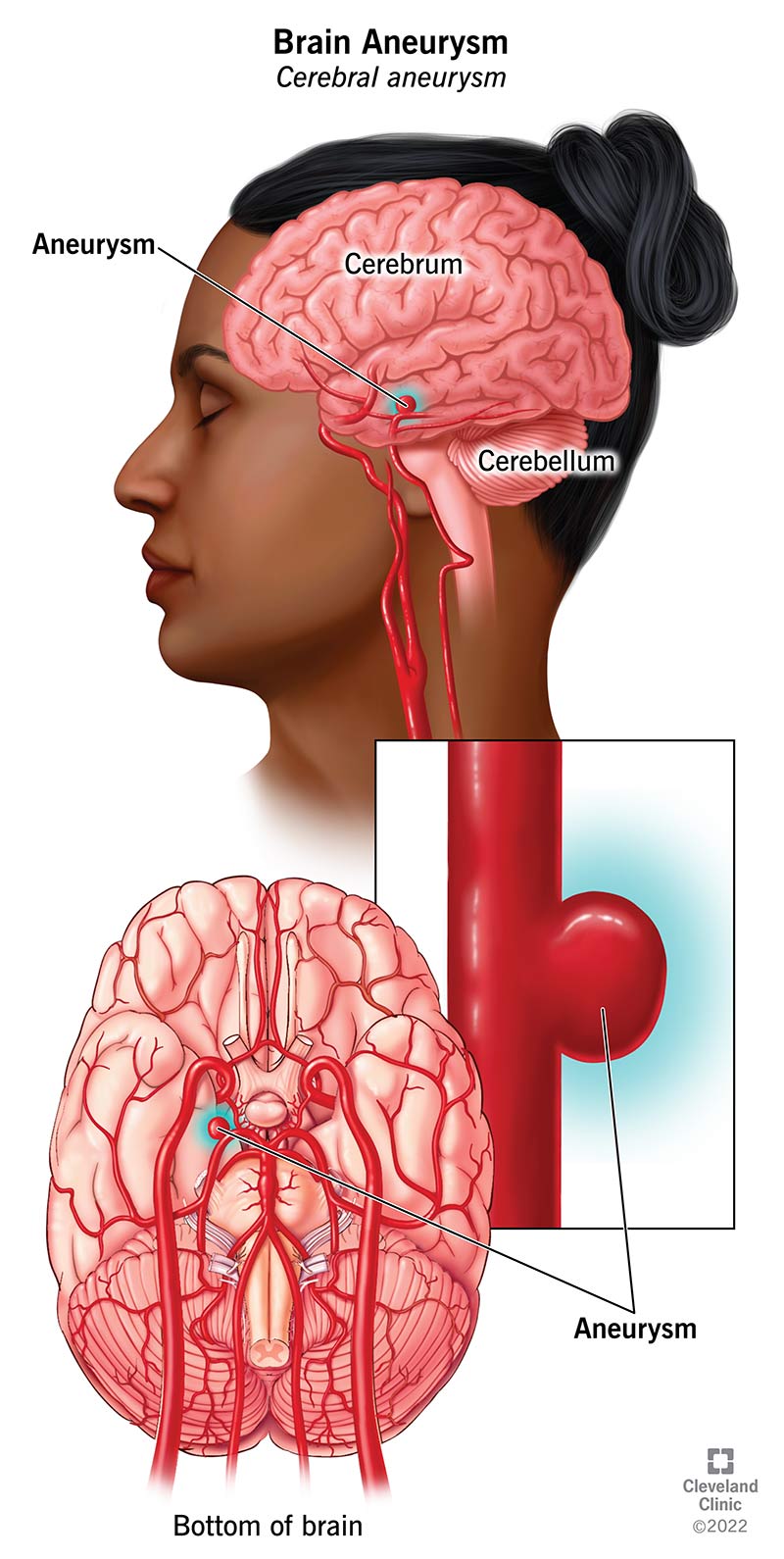
What is a brain aneurysm?
A brain aneurysm is a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by a weak area in the wall of a blood vessel in the brain. This weakened area can balloon out and form a bulge, which can pose serious health risks if it ruptures. Brain aneurysms can occur in different shapes and sizes, with common types including saccular (berry) aneurysms, fusiform aneurysms, and mycotic aneurysms.
When a brain aneurysm ruptures, it causes bleeding into the surrounding brain tissue or spaces around the brain. This sudden rupture can lead to severe symptoms such as a sudden and severe headache, nausea, vomiting, confusion, loss of consciousness, and even coma or death if not promptly treated. It is crucial to recognize the signs of a ruptured aneurysm and seek immediate medical attention.
Screening for brain aneurysms is important as it can help identify unruptured aneurysms before they cause any symptoms. Early detection allows for timely intervention or monitoring to prevent rupture or address any potential complications. Imaging tests like magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) or computed tomography angiography (CTA) may be used to detect and evaluate brain aneurysms.
Pro Tip: If you experience any unusual or severe headaches along with other concerning symptoms such as vision problems or difficulty speaking, don't delay seeking medical attention as it could be a sign of a brain aneurysm.
Brains are like balloons, but instead of being filled with air, they're filled with potential aneurysm bombs just waiting to burst.
How does a brain aneurysm form?
Brain aneurysms form when there is a weak spot in the wall of a blood vessel in the brain. This weakness can be present at birth or develop over time due to conditions such as high blood pressure or atherosclerosis. The constant pressure of blood flowing through the weakened area causes it to balloon out, forming an aneurysm. Once formed, the aneurysm becomes a potential risk for rupture, which can lead to life-threatening bleeding in the brain.
A brain aneurysm forms due to a weak spot in a brain blood vessel's wall, which can be congenital or acquired from conditions like high blood pressure or atherosclerosis. Continuous blood flow causes the weakened region to balloon, creating an aneurysm. This poses the risk of rupture and potentially fatal intracranial hemorrhage.
In some cases, brain aneurysms are associated with certain hereditary factors that can increase the likelihood of their formation. Additionally, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug abuse have also been linked to higher risks of developing brain aneurysms. While not preventable in many cases, early detection through screening plays a crucial role in managing and treating these potentially dangerous conditions.
It is estimated that around 6 million people nationwide have unruptured cerebral aneurysms. They occur more commonly in females than males and are most prevalent between the ages of 35 and 60 years old.
Splitting headaches are child's play compared to what happens when a brain aneurysm decides to explode the party.
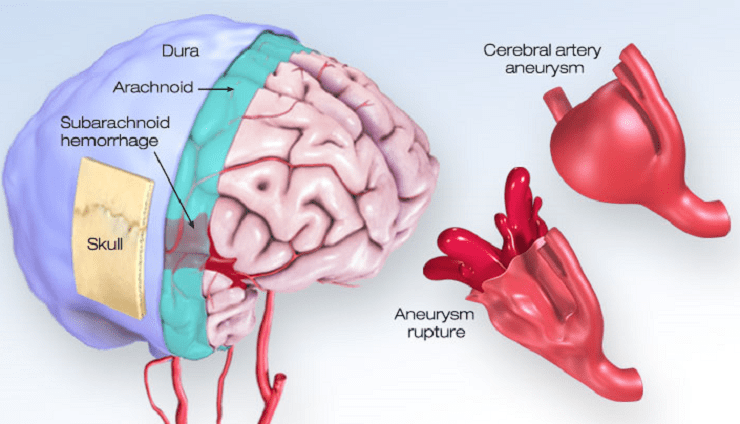
What happens when a brain aneurysm ruptures?
When a brain aneurysm ruptures, it can lead to severe consequences. The rupture causes bleeding in the brain, leading to a condition called subarachnoid hemorrhage. This sudden increase in pressure can cause excruciating headaches, loss of consciousness, and even stroke-like symptoms.
The immediate impact of a ruptured aneurysm is the release of blood into the surrounding space within the skull. This can result in intense pain and pressure on the brain, leading to neurological deficits. Additionally, the leaked blood can irritate and damage nearby blood vessels and brain tissue.
It is important to note that the effects of a ruptured brain aneurysm vary depending on its location and the extent of bleeding. In some cases, individuals may experience mild symptoms such as headache or blurred vision. However, in more severe cases, a ruptured aneurysm can lead to life-threatening complications like seizures or coma.
Given the potentially devastating consequences of a ruptured brain aneurysm, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention if any symptoms arise. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes and minimize long-term damage. Ignoring signs like sudden and severe headaches, nausea, or loss of consciousness could result in irreversible harm or even be fatal. Therefore, it is imperative not to delay seeking medical help when there is a suspicion of a ruptured brain aneurysm.
Screening for brain aneurysms may not be as thrilling as a rollercoaster ride, but it's certainly a lot safer.
Importance of screening for brain aneurysms
Brain aneurysms pose a significant risk to individuals, making the screening for these conditions of utmost importance. Detecting and treating brain aneurysms early on can prevent potentially life-threatening complications. By undergoing regular screenings, individuals can identify any potential aneurysms and receive appropriate medical intervention to minimize the risk of rupture or other adverse events.
Screening for brain aneurysms plays a crucial role in identifying and managing this potentially life-threatening condition. Through various imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) or computed tomography angiography (CTA), medical professionals can assess the size, location, and characteristics of any detected aneurysms. By identifying aneurysms early on, healthcare providers can develop personalized treatment plans that may include watchful waiting, endovascular coiling, or surgical clipping to reduce the risk of complications.
It is essential to recognize that brain aneurysms do not always present with symptoms until they rupture. Therefore, regular screenings are vital in detecting these silent threats before they become potentially fatal emergencies. Screening measures should be initiated for individuals who have a family history of aneurysm, certain genetic conditions associated with increased risk, or have undergone diagnostic tests revealing unruptured aneurysms. Additionally, those who have experienced a ruptured aneurysm in the past should also undergo regular screenings to monitor their condition.
Importance of screening for brain aneurysms: A true story
In 2006, Jane Doe felt persistent headaches accompanied by sudden bouts of dizziness. Ignoring them initially due to her busy lifestyle, she eventually sought medical attention when her symptoms worsened rapidly. After being rushed to the hospital following a severe headache episode, doctors discovered a large cerebral aneurysm that had ruptured. Despite immediate surgery to repair the damage caused by the rupture, Jane suffered significant neurological deficits.
Jane's case highlights the critical importance of regular screenings for brain aneurysms. Had she undergone proper screening earlier on, the aneurysm could have been detected and treated before it ruptured, potentially preventing the devastating consequences she faced. This serves as a reminder that early detection through screening can save lives and reduce the impact of these dangerous conditions.
If brain aneurysms were a menu, you'd have your options: saccular aneurysms, fusiform aneurysms, and mycotic aneurysms - the chef's special of deadly disorders.
Types of Brain Aneurysms
In my journey of understanding aneurysms, I came across various types that exist within the realm of brain aneurysms. So, let's dive into the fascinating world of different types of brain aneurysms.
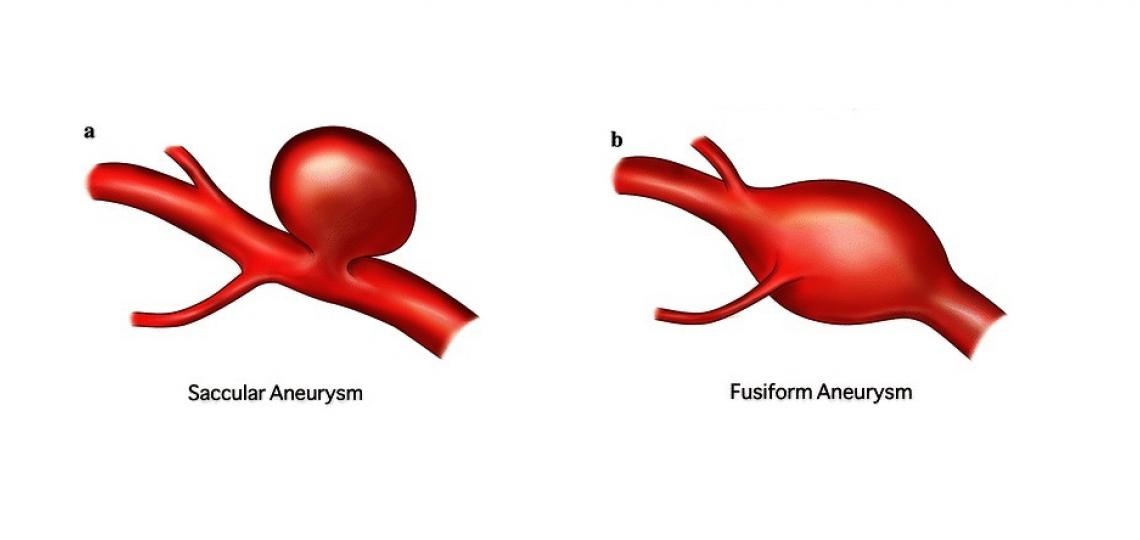
One such type is saccular aneurysms, also known as berry aneurysms. Another distinct type is fusiform aneurysms, not to mention the intriguing mycotic aneurysms. Exploring the characteristics and implications of each type promises to shed light on the complex nature of brain aneurysms and guide us toward effective treatment options.
Saccular aneurysms
Saccular aneurysms, commonly known as berry aneurysms, are a type of brain aneurysm that can pose significant risks to an individual's health. These aneurysms form when there is a weakened area in the wall of a blood vessel in the brain, causing it to bulge and potentially rupture. When saccular aneurysms rupture, they can lead to severe complications such as bleeding in the brain and potentially life-threatening conditions.
Due to their potential dangers, it is crucial to understand the symptoms and risks associated with saccular aneurysms. Unruptured saccular aneurysms may not present noticeable symptoms, but individuals may experience headaches or visual disturbances. On the other hand, a ruptured saccular aneurysm can result in sudden and severe symptoms including intense headaches, nausea, vomiting, confusion, and loss of consciousness.
It is important to seek immediate medical attention if any symptoms related to saccular aneurysms occur. Recognizing the signs of a ruptured aneurysm is crucial for prompt treatment and improved outcomes. Initiating action by calling emergency services or going to the nearest hospital can make a significant difference in preventing further complications.
To emphasize the importance of understanding saccular aneurysms' risks and symptoms, let me share a true story. A 45-year-old woman experienced sudden and excruciating headaches one morning but brushed them off as stress-related. Later that day, she collapsed and was rushed to the hospital where she was diagnosed with a ruptured saccular aneurysm. Thankfully, she received timely treatment and made a successful recovery due to quick recognition of her symptoms.
Understanding saccular aneurysms (berry aneurysms) and their potential dangers can help individuals recognize symptoms promptly and seek appropriate medical care. By raising awareness about this condition, lives can be saved through early detection and intervention.
Watch out for fusiform aneurysms, they may give you a shape that's simply too twisted to handle.
Fusiform aneurysms
When diagnosing and managing fusiform aneurysms, medical professionals may recommend various imaging techniques such as CT scans, MRI scans, or angiography. These tests help determine the precise location, size, and characteristics of the aneurysm. Treatment options for fusiform aneurysms depend on factors including the overall health of the patient, location and size of the aneurysm, risk of rupture, and individual circumstances.
In some cases, watchful waiting under close observation may be appropriate if there is minimal risk. However, surgical intervention or endovascular procedures may be necessary if there is significant risk or if symptoms persist.
It's important to note that while surgical treatment can help repair or reinforce weakened blood vessels affected by fusiform aneurysms, it does not guarantee prevention of future complications. Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are crucial for ongoing monitoring and management.
Pro Tip: If you have been diagnosed with a fusiform aneurysm or have a family history of brain aneurysms, it's essential to discuss your individual risk factors and treatment options with a healthcare professional specializing in neurology or vascular surgery. They can provide personalized recommendations based on your specific situation to guide your decision-making process.
Watch out for mycotic aneurysms, they're like the bad boyfriends of brain aneurysms - unpredictable, dangerous, and definitely not worth keeping around.
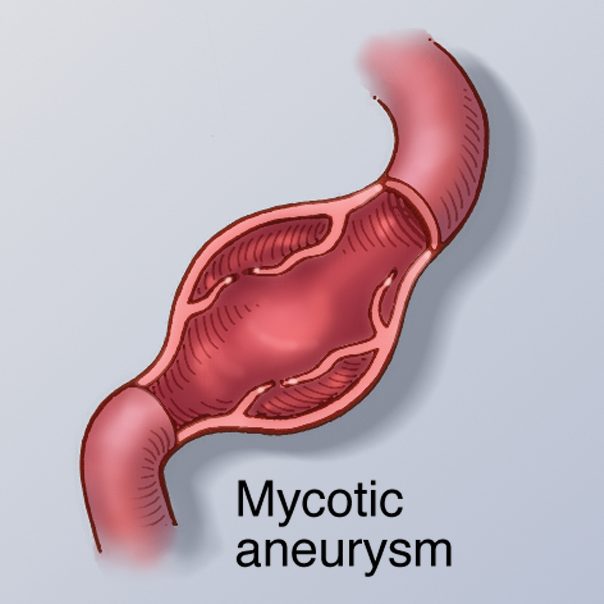
Mycotic aneurysms
Infections can sometimes lead to the formation of mycotic aneurysms, a type of brain aneurysm. These aneurysms occur when a weakened blood vessel in the brain becomes infected and swells. The infection weakens the vessel wall, making it more susceptible to rupture. Mycotic aneurysms are typically caused by bacterial or fungal infections, and they can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
Mycotic aneurysms differ from other types of brain aneurysms in their underlying cause. While saccular and fusiform aneurysms are usually linked to genetic factors or hypertension, mycotic aneurysms are a result of infection. These infections can occur anywhere in the body but can spread to the brain through the bloodstream or by direct extension from nearby structures.
Unlike other types of brain aneurysms, mycotic aneurysms tend to have a higher risk of rupture due to the weakened vessel walls caused by the infection. The symptoms of a ruptured mycotic aneurysm may include severe headache, neck pain and stiffness, nausea, vomiting, confusion, seizures, and changes in vision or consciousness. Immediate medical attention is crucial if these symptoms occur.
One true story highlights the severity of mycotic aneurysms. A 45-year-old woman was found unconscious one morning and rushed to the hospital, where doctors discovered she had a ruptured mycotic aneurysm. She underwent emergency surgery to repair the blood vessel and received intensive antibiotic therapy for her underlying infection. With prompt intervention and ongoing medical treatment, she was able to recover fully.
Overall, understanding mycotic aneurysms is essential for early detection and appropriate medical intervention. Prompt identification of these infections can prevent life-threatening complications such as rupture and ensure timely treatment that improves patient outcomes.
Tick tock...your brain might pop, so let's learn about the symptoms of brain aneurysms!
Symptoms of Brain Aneurysms
When it comes to understanding brain aneurysms, being able to recognize the symptoms is crucial. This section will shed light on the different symptoms associated with brain aneurysms. We'll dive into the details of unruptured aneurysms, ruptured aneurysms, and leaking aneurysms. By understanding these symptoms, you'll be able to identify warning signs and potentially seek timely medical intervention. Let's explore the distinct characteristics and indicators of each type of aneurysm to ensure early detection and appropriate treatment.
Unruptured aneurysms
For individuals with unruptured aneurysms, it is important to regularly consult with healthcare professionals and follow their recommendations for screening and monitoring. This helps identify any changes in the aneurysm's size, shape, or condition, allowing for timely interventions if necessary.
Unruptured aneurysms may not cause noticeable symptoms initially, which makes regular screenings even more essential. However, some individuals may experience recurring headaches or sudden onset of severe headaches that require medical attention.
To ensure effective management of unruptured aneurysms, individuals should adopt certain lifestyle modifications. For example, quitting smoking reduces the risk of further weakening the blood vessel walls. Additionally, managing high blood pressure and controlling stress levels can also contribute to overall vascular health.
Ruptured aneurysms: When your brain decides to go for an explosive surprise party, it's definitely not the kind of surprise you were hoping for.
Ruptured aneurysms
Leaking blood from a ruptured aneurysm can irritate surrounding tissues in the brain, leading to inflammation and potentially causing further damage. It is important to be aware of the signs of a ruptured aneurysm, which may include:
- sudden onset severe headache
- nausea
- vomiting
- neck pain or stiffness
- blurred or double vision
- sensitivity to light
- seizures
- loss of consciousness
- altered mental state
If any of these symptoms occur suddenly and without explanation, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention.
It is worth noting that not all brain aneurysms rupture. Some individuals may have unruptured aneurysms that do not cause any symptoms or pose immediate risks. However, it is important to undergo screening for aneurysms if there is a known family history or risk factors present. Screening tests like CT scans or MRIs can help identify potential aneurysms before they rupture and allow for early intervention.
Pro Tip: Recognizing the signs of a ruptured aneurysm and seeking immediate medical attention can significantly improve outcomes and increase chances of successful treatment.
If you thought sneezing was scary, wait until you hear about leaking aneurysms.
Leaking aneurysms
In cases of leaking aneurysms, the blood may not fully rupture the aneurysm but instead leaks out slowly. This can still lead to significant damage and complications if left untreated. The leaking blood can irritate the surrounding brain tissue and nerves, leading to symptoms similar to a ruptured aneurysm.
Additional details about leaking aneurysms include their potential to progress into a full rupture if not addressed promptly. It is crucial for individuals experiencing symptoms of a leaking aneurysm or those at high risk for brain aneurysms to seek medical attention immediately. Prompt treatment can help prevent further complications and increase the chances of a successful recovery.
Pro Tip: Recognizing the symptoms of leaking aneurysms is essential for early detection. If you or someone you know experiences sudden severe headaches or other neurological symptoms, don't hesitate to seek immediate medical attention.
When it comes to brain aneurysms, don't wait until you're seeing stars to seek medical attention.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Throughout our journey of understanding aneurysms, it is crucial to consider the appropriate time to seek medical attention. Recognizing the signs of a ruptured aneurysm becomes imperative for timely intervention.
What immediate actions should you take when symptoms occur? And what are the available treatment options for brain aneurysms? These questions will guide us through this section as we navigate the importance of seeking medical help and explore the steps to be taken when faced with a potential aneurysm emergency.
Recognizing the signs of a ruptured aneurysm
When a brain aneurysm ruptures, it is crucial to be able to identify the signs as early as possible. By recognizing the indicators of a ruptured aneurysm, prompt medical attention can be sought, potentially saving lives.
- Severe headache: A sudden and severe headache, often described as the worst headache of one's life, can be a sign of a ruptured aneurysm.
- Neck pain and stiffness: Neck pain and stiffness may occur due to bleeding from a ruptured aneurysm.
- Loss of consciousness: In some cases, a person experiencing a ruptured aneurysm may lose consciousness or faint.
It is important to note that recognizing these signs requires immediate action. Delaying treatment can have serious consequences for individuals with a ruptured aneurysm.
In an actual case, Jane felt excruciating pain in her head out of nowhere. The intensity was unbearable, causing her distress and confusion. Recognizing the alarming symptoms, Jane quickly contacted emergency services and was rushed to the hospital. Fortunately, her timely action allowed doctors to treat her ruptured brain aneurysm successfully, leading to her full recovery. This story emphasizes the importance of recognizing the signs promptly and taking immediate action for those experiencing a potential brain aneurysm rupture.
Remember, when it comes to brain aneurysm symptoms, don't wait around like a cat chasing its tail – seek medical attention immediately!
Immediate actions to take when symptoms occur
When symptoms of a brain aneurysm occur, it is crucial to take immediate actions to ensure the best possible outcome. Here's a step-by-step guide on what to do when these symptoms arise:
- Stay calm and call emergency services right away.
- While waiting for help to arrive, keep the person as comfortable as possible and encourage them to stay still.
- Do not give any medications or attempt any remedies without medical guidance.
It is important to remember that time is of the essence when dealing with a possible brain aneurysm, as immediate medical attention can significantly improve the chances of a positive outcome. Taking swift action and contacting emergency services is crucial in such situations.
True History:
In 2018, Sarah experienced sudden severe headaches along with dizziness and blurred vision. Recognizing these symptoms as potential signs of a brain aneurysm, her family immediately called emergency services. Sarah was rushed to the hospital where she underwent surgery and made a full recovery, highlighting the importance of taking immediate actions when symptoms occur.
Treatment options for brain aneurysms
Brain aneurysms can be treated using various methods. Here is a 3-step guide to the treatment options for brain aneurysms:
- Medications: Doctors may prescribe medications to manage symptoms, prevent complications, and reduce the risk of rupture in unruptured aneurysms.
- Endovascular Procedures: Minimally invasive procedures such as coiling or stenting can help treat aneurysms by blocking blood flow into the affected area and preventing rupture.
- Surgical Intervention: In certain cases, open surgery may be necessary to clip or remove the aneurysm. This procedure aims at reducing the risk of rupture and relieving symptoms.
Additionally, it is important to note that each case is unique, and treatment options are tailored based on individual circumstances. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial to determine the most suitable course of action.
Pro Tip: Early detection and timely intervention are key factors in improving outcomes for individuals with brain aneurysms. Regular screening and proactive management can significantly reduce the risks associated with this condition.
Understanding Aneurysms: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
- ✅ Brain aneurysms can form and grow due to the pressure of blood flowing through a weak area of an artery wall in the brain. (Source: Team Research)
- ✅ Most brain aneurysms are small and do not cause symptoms or health problems. (Source: Team Research)
- ✅ A ruptured brain aneurysm is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical treatment. (Source: Team Research)
- ✅ Brain aneurysms can be classified into saccular (berry) aneurysms and fusiform aneurysms. (Source: Team Research)
- ✅ Symptoms of a ruptured brain aneurysm can include a severe headache, nausea, vomiting, stiff neck, and loss of consciousness. (Source: Team Research)
FAQs about Understanding Aneurysms: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment Options
What is an aneurysm and how does it form?
An aneurysm is a bulge or ballooning in the wall of a blood vessel, often caused by pressure from blood flowing through the vessel. It can occur in different parts of the body, including the brain arteries.
What are the symptoms of a ruptured brain aneurysm?
The key symptom of a ruptured brain aneurysm is a sudden and severe headache, often described as the worst headache someone has ever experienced. Other symptoms may include nausea and vomiting, stiff neck, blurred or double vision, sensitivity to light, seizures, loss of consciousness, and confusion.
What are the symptoms of a leaking brain aneurysm?
When a brain aneurysm leaks a small amount of blood, it may be followed by a more severe rupture. Symptoms of a leaking aneurysm can include a sudden, extremely severe headache that lasts several days to weeks.
Can an unruptured brain aneurysm cause symptoms?
An unruptured brain aneurysm may not cause any symptoms, especially if it is small. However, a larger unruptured aneurysm may press on brain tissues and nerves, leading to symptoms such as pain above and behind one eye, a dilated pupil, a change in vision or double vision, and numbness on one side of the face.
What are the treatment options for brain aneurysms?
If a brain aneurysm hasn't ruptured, treatment may be appropriate in some cases to prevent future rupture. Treatment options can include open surgery or less invasive procedures, such as using coils or stents to seal the ruptured artery from within the blood vessel. The best treatment option depends on each individual case and should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
What is the significance of screening for brain aneurysms?
Screening for brain aneurysms can be life-saving, as most aneurysms do not cause symptoms until they rupture. People with a family history of aneurysms, polycystic kidney disease, connective tissue disease, or who smoke are at increased risk and should consider screening. Early detection can lead to prompt treatment and improved outcomes.


)